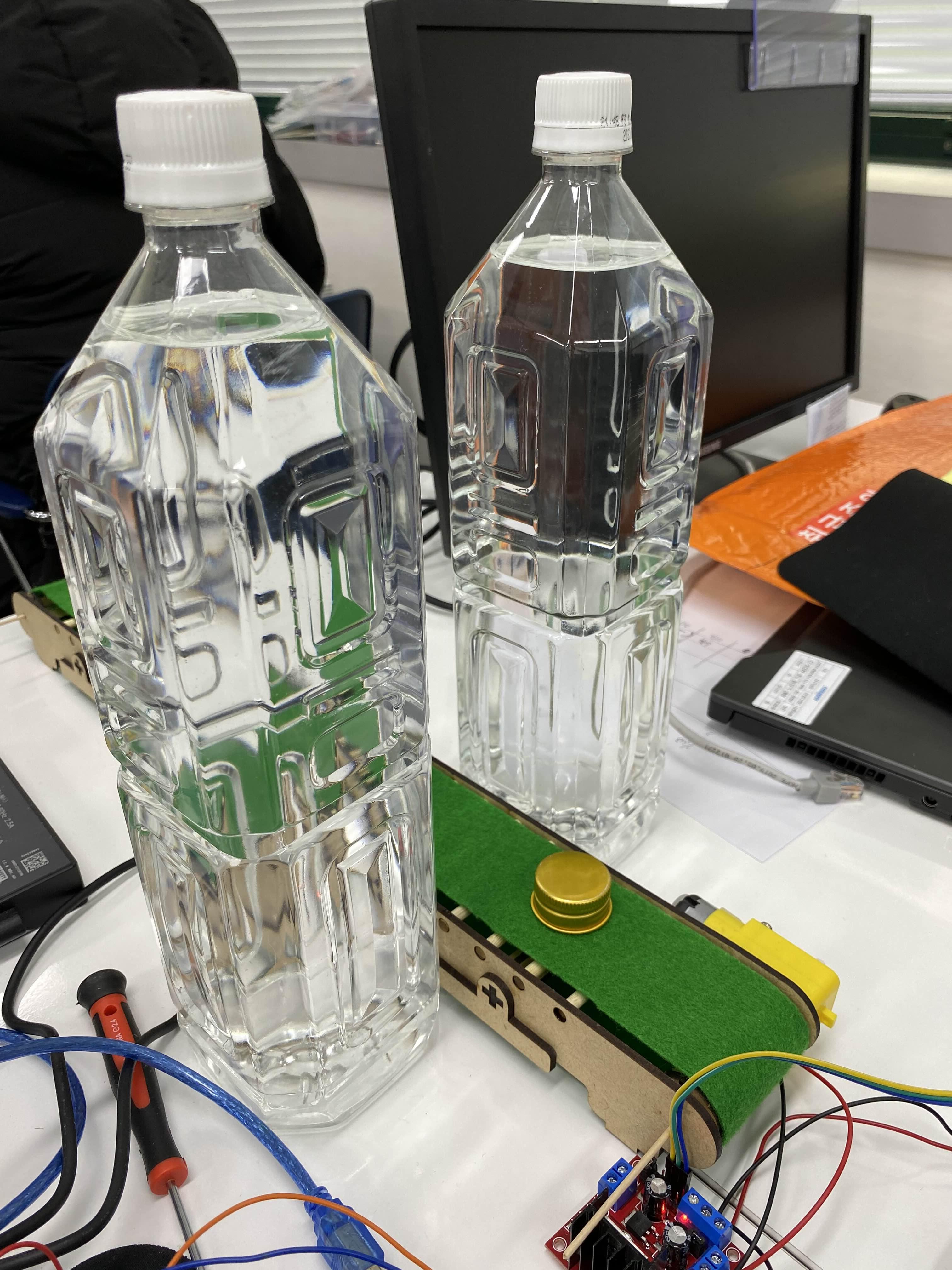

이렇게 해서 카메라를 위에 올리자..
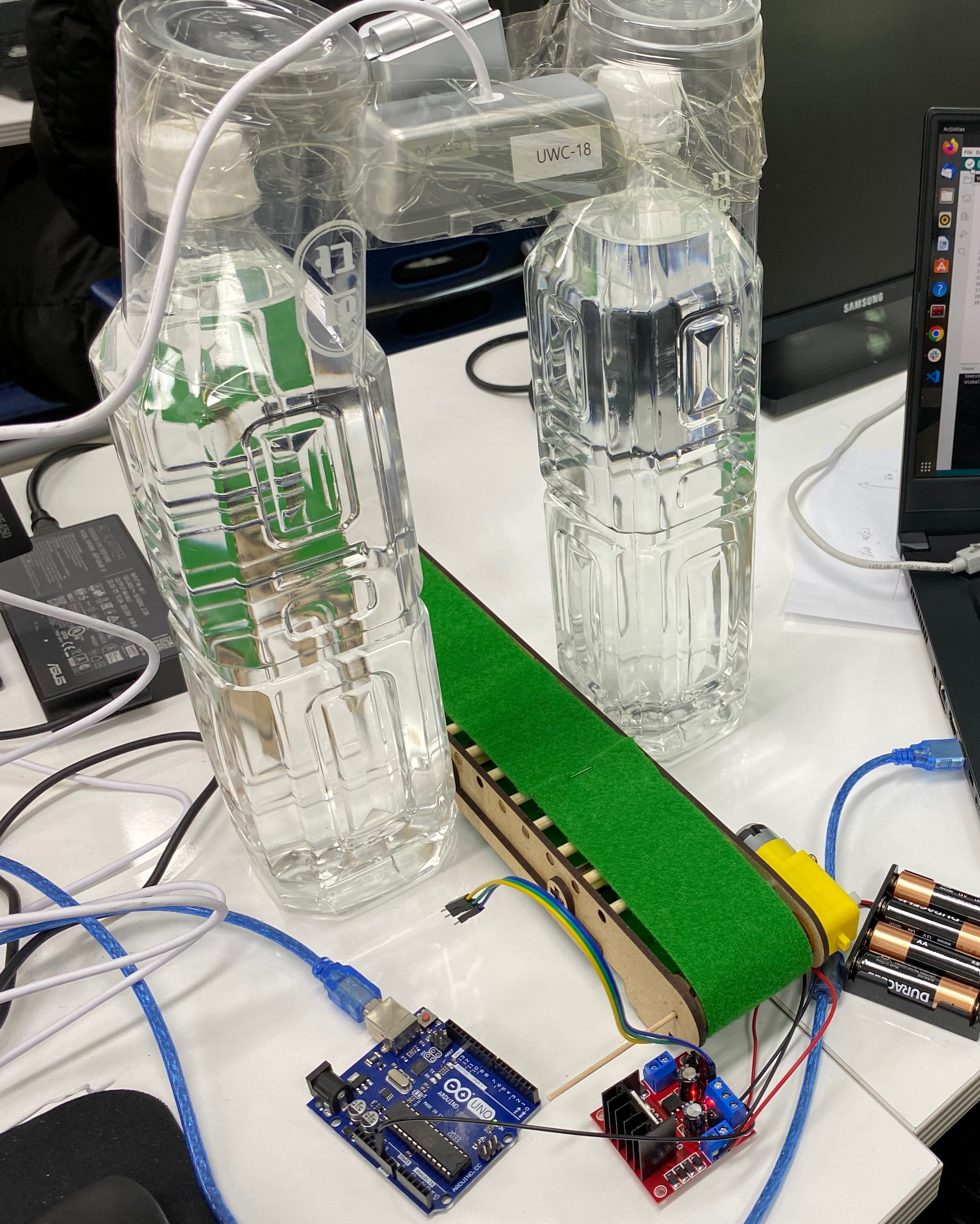

완성..
디자인은 아직 설계단계니까..
컨베이어 벨트 코드
이걸 굴리면서
적절한 값을 찾아야겠다.
bool is_start = 0;
void setup() {
// put your setup code here, to run once:
pinMode(4, 1);
pinMode(5, 1);
}
void loop() {
if (is_start == 0) {
digitalWrite(4, 1); // 5V : +
digitalWrite(5, 0); // GND (0V) :-
analogWrite(3, 255);
delay(50);
is_start = 1;
}
// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:
digitalWrite(4, 1); // 5V : +
digitalWrite(5, 0); // GND (0V) :-
analogWrite(3, 255/4);
}이건 적절한 파라미터 값을 찾기위해서 하는 것
import sys
import numpy as np
import cv2
#import serial
import time
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
if not cap.isOpened():
print("열리지 않아요")
sys.exit()
#ser = serial.Serial('/dev/ttyACM0', 9600)
count = 0
de_count = 0
radius_list = []
while True:
ret, frame = cap.read()
if not ret:
break
#src = cv2.resize(frame, dsize=(900, 959))
# 이미지의 사이즈를 조절한다.
gray = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
blr = cv2.GaussianBlur(gray, (0, 0), 1.0)
# 이미지의 잡음을 제거한다.
# 실질적인 허프변환이 시작되는 부분
circles = cv2.HoughCircles(blr, cv2.HOUGH_GRADIENT, 1, 50, param1=120, param2=40, minRadius=10, maxRadius=80)
# 반지름과 threshold를 조절하면서 확인해볼 분이다.
dst = frame.copy()
# 이미지를 복사해서 dst에 저장한다.
cv2.imshow('img', frame)
# 원을 검출할 때 실행된다.
if circles is not None:
#for i in range(circles.shape[1]):
# 검출된 원의 개수만큼 돌아서 원을 그린다.
cx, cy, radius = circles[0][0]
cv2.circle(dst, (int(cx), int(cy)), int(radius), (255, 0, 0), 2, cv2.LINE_AA)
cv2.putText(dst, str(radius), org=(int(cx), int(cy)),
fontFace=cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, fontScale=1,
color=(0,0,255),thickness=3, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
radius_list.append(radius)
time.sleep(0.25)
else:
de_count += 1
if de_count == 5:
if len(radius_list) > 1:
print(radius_list)
radius_list = []
de_count = 0
cv2.imshow('img', dst)
key = cv2.waitKey(1)
if key == 27:
break
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
0.1초마다 원을 디텍션
결과값을 복사해서
[21.6, 22.3, 15.0, 36.1, 21.0, 36.0, 65.1, 68.3, 35.9, 36.0, 20.5, 66.2, 70.5, 21.0, 27.5, 29.4, 24.1, 24.1, 25.4, 26.6, 26.7, 27.7, 28.5, 26.6, 28.5, 28.9, 27.4, 26.4, 26.4, 28.0, 27.8, 28.9, 28.9, 27.8, 28.0, 28.4, 28.4, 28.9, 28.8, 28.2, 29.9, 30.2, 30.5, 30.1, 28.9]import numpy as np
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltlist = [21.6, 22.3, 15.0, 36.1, 21.0, 36.0, 65.1, 68.3, 35.9, 36.0, 20.5, 66.2, 70.5, 21.0, 27.5, 29.4, 24.1, 24.1, 25.4, 26.6, 26.7, 27.7, 28.5, 26.6, 28.5, 28.9, 27.4, 26.4, 26.4, 28.0, 27.8, 28.9, 28.9, 27.8, 28.0, 28.4, 28.4, 28.9, 28.8, 28.2, 29.9, 30.2, 30.5, 30.1, 28.9]
print(len(list))
print(np.average(list))
시각화까지 진행하자.
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
sns.boxplot(x=list, orient='h')
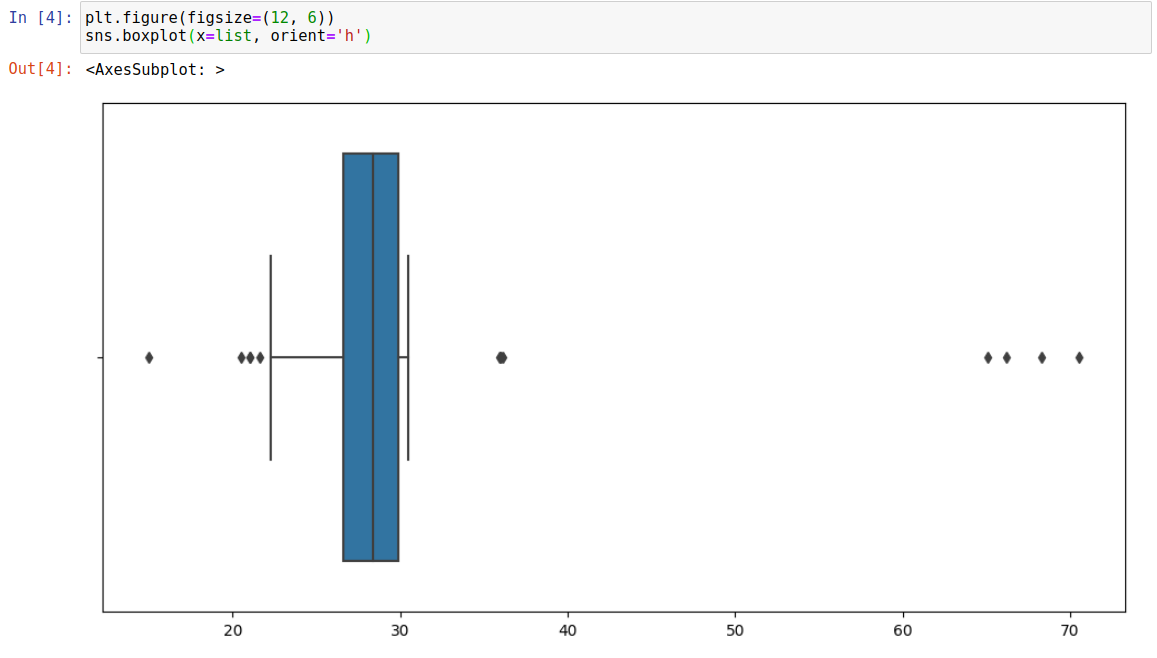
박스안에 들어가는 값이 진짜 값이다.
그래서 원을 어떻게 접근해야할까
평균으로 접근하면 위험성이 생긴다.
박스안에 들어가는 경우 카운트를 하는거로 구현하는게 맞지 않을까?
일단 원을 디텍션하는 시간을 0.25초로 줄여보고 진행해보자.
[23.2, 28.6, 28.9, 26.1, 26.6, 28.8, 27.4, 25.8, 27.5, 25.7, 26.7, 29.2, 28.8, 28.9, 29.7, 29.7]이를 시각화해보자.
list = [23.2, 28.6, 28.9, 26.1, 26.6, 28.8, 27.4, 25.8, 27.5, 25.7, 26.7, 29.2, 28.8, 28.9, 29.7, 29.7]
print(len(list))
print(np.average(list))
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
sns.boxplot(x=list, orient='h')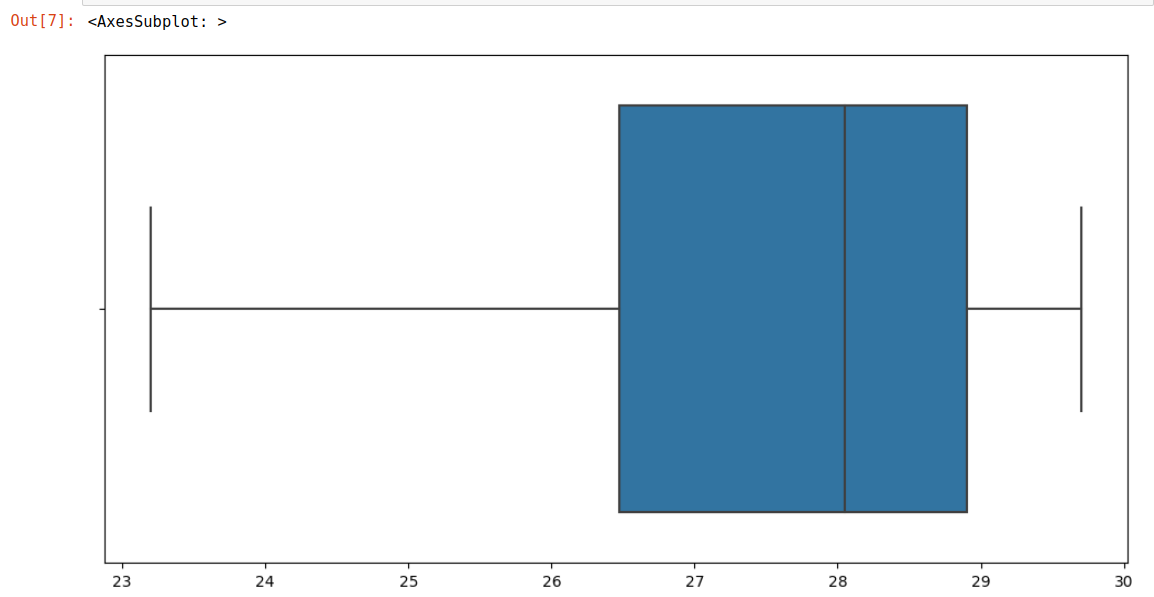
일단 평균은 박스플롯안에 들어간다.
0.25초로 줄였을때 이상치가 상당히 많이 줄어드는 것으로 보인다.
그러면 0.25초로 확정하기 위해서 5번 정도 측정을 해보고 boxplot 을 그려본다.
총 9번의 측정결과
[23.0, 26.6, 25.7, 29.9, 24.0, 24.3, 25.8, 26.6, 26.8, 29.6, 28.4, 29.7, 28.8, 29.9]
[29.1, 28.8, 27.9, 25.4, 24.6, 25.2, 28.6, 30.8, 26.6, 26.7, 26.3, 26.7, 28.4, 30.2, 29.6, 29.3, 28.6]
[24.9, 26.6, 28.6, 24.0, 27.1, 27.1, 26.3, 26.3, 30.2, 29.1, 29.0, 29.9, 28.4]
[27.4, 26.3, 28.6, 25.0, 29.3, 27.4, 25.8, 25.2, 25.7, 25.7, 27.4, 28.6, 29.3, 29.0, 28.8, 29.1]
[25.4, 25.2, 24.3, 26.6, 24.5, 25.7, 25.2, 26.6, 30.2, 29.0, 29.9, 31.4, 30.8]
[24.6, 25.2, 25.4, 24.6, 24.6, 25.0, 25.2, 26.0, 26.4, 27.0, 29.3, 28.9, 29.6, 29.7, 30.8, 29.4]
[26.3, 27.4, 24.1, 25.0, 26.6, 26.4, 26.4, 26.8, 28.5, 29.9, 29.6, 28.0]
[24.3, 24.5, 25.8, 25.2, 24.6, 28.8, 29.1, 27.8, 27.7, 29.1, 28.8, 28.6, 28.0]
[28.9, 25.2, 25.4, 22.3, 24.6, 25.4, 25.2, 25.8, 26.4, 26.3, 27.1, 26.7, 28.2, 28.4, 28.8, 28.8, 30.5]쥬피터에 넣고 돌리자
list = [[23.0, 26.6, 25.7, 29.9, 24.0, 24.3, 25.8, 26.6, 26.8, 29.6, 28.4, 29.7, 28.8, 29.9],
[29.1, 28.8, 27.9, 25.4, 24.6, 25.2, 28.6, 30.8, 26.6, 26.7, 26.3, 26.7, 28.4, 30.2, 29.6, 29.3, 28.6],
[24.9, 26.6, 28.6, 24.0, 27.1, 27.1, 26.3, 26.3, 30.2, 29.1, 29.0, 29.9, 28.4],
[27.4, 26.3, 28.6, 25.0, 29.3, 27.4, 25.8, 25.2, 25.7, 25.7, 27.4, 28.6, 29.3, 29.0, 28.8, 29.1],
[25.4, 25.2, 24.3, 26.6, 24.5, 25.7, 25.2, 26.6, 30.2, 29.0, 29.9, 31.4, 30.8],
[24.6, 25.2, 25.4, 24.6, 24.6, 25.0, 25.2, 26.0, 26.4, 27.0, 29.3, 28.9, 29.6, 29.7, 30.8, 29.4],
[26.3, 27.4, 24.1, 25.0, 26.6, 26.4, 26.4, 26.8, 28.5, 29.9, 29.6, 28.0],
[24.3, 24.5, 25.8, 25.2, 24.6, 28.8, 29.1, 27.8, 27.7, 29.1, 28.8, 28.6, 28.0],
[28.9, 25.2, 25.4, 22.3, 24.6, 25.4, 25.2, 25.8, 26.4, 26.3, 27.1, 26.7, 28.2, 28.4, 28.8, 28.8, 30.5]],
for i in list[0]:
print("길이 : " + str(len(i)) + "평균 : " + str(np.average(i)))
print("boxplot 시작점 : " + str(np.percentile(i, 25)) + "boxplot 끝점 : " + str(np.percentile(i, 75)))
print("------------")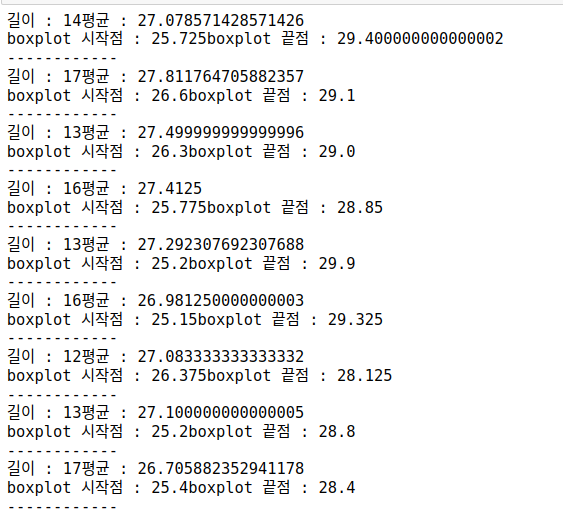
그러면
불량 판단기준을 25 ~29.5로 잡고
원이 10개가 검출되었을때의 평균이
25~29.5 범위안에 들어왔다면 정상으로 판단하고
그 외라면 불량으로 판단하자
그러면 코드를 잠시 수정해보자.
직접 컨베이어 벨트를 돌려보면서 측정한 결과

약간의 수정이 필요했다.
25~29.5 범위로 할 경우
컨베이어 속도가 일정하지 않아서 정상을 불량으로 판단하는 경우가 생겼다.
그래서
25~31범위로 설정했다.
그리고 화면상에 정상, 비정상여부와 반지름을 출력하게 만들었다.
import sys
import numpy as np
import cv2
import time
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
if not cap.isOpened():
print("열리지 않아요")
sys.exit()
#ser = serial.Serial('/dev/ttyACM0', 9600)
count = 0
de_count = 0
radius_list = []
munjang = "not detect"
R = 255
G = 255
B = 255
while True:
ret, frame = cap.read()
if not ret:
break
gray = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
blr = cv2.GaussianBlur(gray, (0, 0), 1.0)
# 이미지의 잡음을 제거한다.
# 실질적인 허프변환이 시작되는 부분
circles = cv2.HoughCircles(blr, cv2.HOUGH_GRADIENT, 1, 50, param1=120, param2=40, minRadius=10, maxRadius=80)
# 반지름과 threshold를 조절하면서 확인해볼 분이다.
dst = frame.copy()
# 이미지를 복사해서 dst에 저장한다.
cv2.imshow('img', frame)
# 원을 검출할 때 실행된다.
if circles is not None:
cv2.putText(dst, munjang, org=(0, 30),
fontFace=cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, fontScale=1,
color=(R,G,B),thickness=1, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
cx, cy, radius = circles[0][0]
cv2.circle(dst, (int(cx), int(cy)), int(radius), (255, 0, 0), 2, cv2.LINE_AA)
cv2.putText(dst, str(radius), org=(int(cx), int(cy)),
fontFace=cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, fontScale=1,
color=(0,0,255),thickness=3, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
radius_list.append(radius)
count += 1
print(count)
if count == 5:
print("디텍션 평균은 : " + str(np.average(radius_list)))
if np.average(radius_list) >= 25 and np.average(radius_list) <= 31:
munjang = "pass (" + str(np.average(radius_list)) + ")"
R = 255
G = 0
B = 255
else:
munjang = "fail (" + str(np.average(radius_list)) + ")"
R = 0
G = 0
B = 255
radius_list.clear()
count = 0
de_count = 0
time.sleep(0.25)
else:
cv2.putText(dst, munjang, org=(0, 30),
fontFace=cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, fontScale=1,
color=(R,G,B),thickness=1, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
de_count += 1
if de_count == 5:
munjang = "not detect"
R = 255
G = 255
B = 255
de_count = 0
count = 0
time.sleep(0.25)
cv2.imshow('img', dst)
key = cv2.waitKey(1)
if key == 27:
break
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
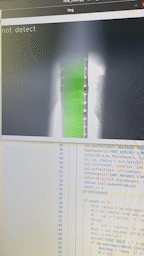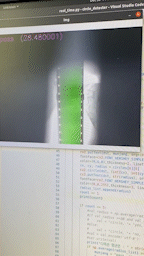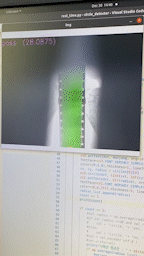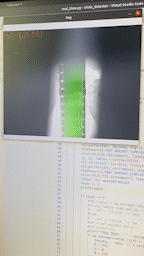
이걸로 측정을 하는 경우 이런식으로 표현된다.
'ㅇ 프로젝트 > TEAM_스마트 팩토리' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 7. 레이저 센서 구현하기 , 초음파 센서 합치기 (0) | 2023.01.02 |
|---|---|
| 6. 서브모터 제작해서 분류완료하기 (0) | 2022.12.30 |
| 4. 원을 검출하고 이를 시리얼 통신으로 아두이노 LCD에 기록하자. (0) | 2022.12.29 |
| 3. 아두이노와 파이썬코드의 시리얼 통신 구현하기 (0) | 2022.12.29 |
| 2. 스마트 팩토리 구체화하기 (0) | 2022.12.27 |